Green Ibex
Knowledge Hub
Step-by-Step Guide: Calculate Your Own Carbon Emissions
Have you ever wished you could X-ray your business, uncovering hidden inefficiencies and spotting opportunities you might have missed? That’s exactly what understanding your company’s carbon emissions can do—help you see where they come from and how to manage them. This blog isn’t about tree planting or tree hugging; it’s about carbon calculation, from A to Z.
Why calculating CO2 emissions is crucial for businesses
Are you looking to improve the efficiency of your operations? If the answer is yes, and you haven’t calculated your CO2 emissions yet – now is the best time to do so. By measuring your carbon footprint, you can identify ways to reduce energy use, which often leads to carbon savings. Going green comes with a lot of benefits.
Understanding how to calculate CO2 emissions not only helps you align with regulatory requirements but also helps in securing major contracts, especially with government clients. For example, in the UK, businesses need a carbon reduction plan to bid on larger government projects (we have covered the nitty-gritty in this blog). Beyond meeting these requirements, focusing on emissions reduction helps improve a company’s reputation and opens the door to new innovations, like renewable energy or streamlined logistics.
Understanding the key components of a business carbon footprint
A business’s carbon footprint is comprised of three main elements, known as ‘scopes’. These scopes help categorise different types of emissions, making it easier for companies to measure and manage their environmental impact.
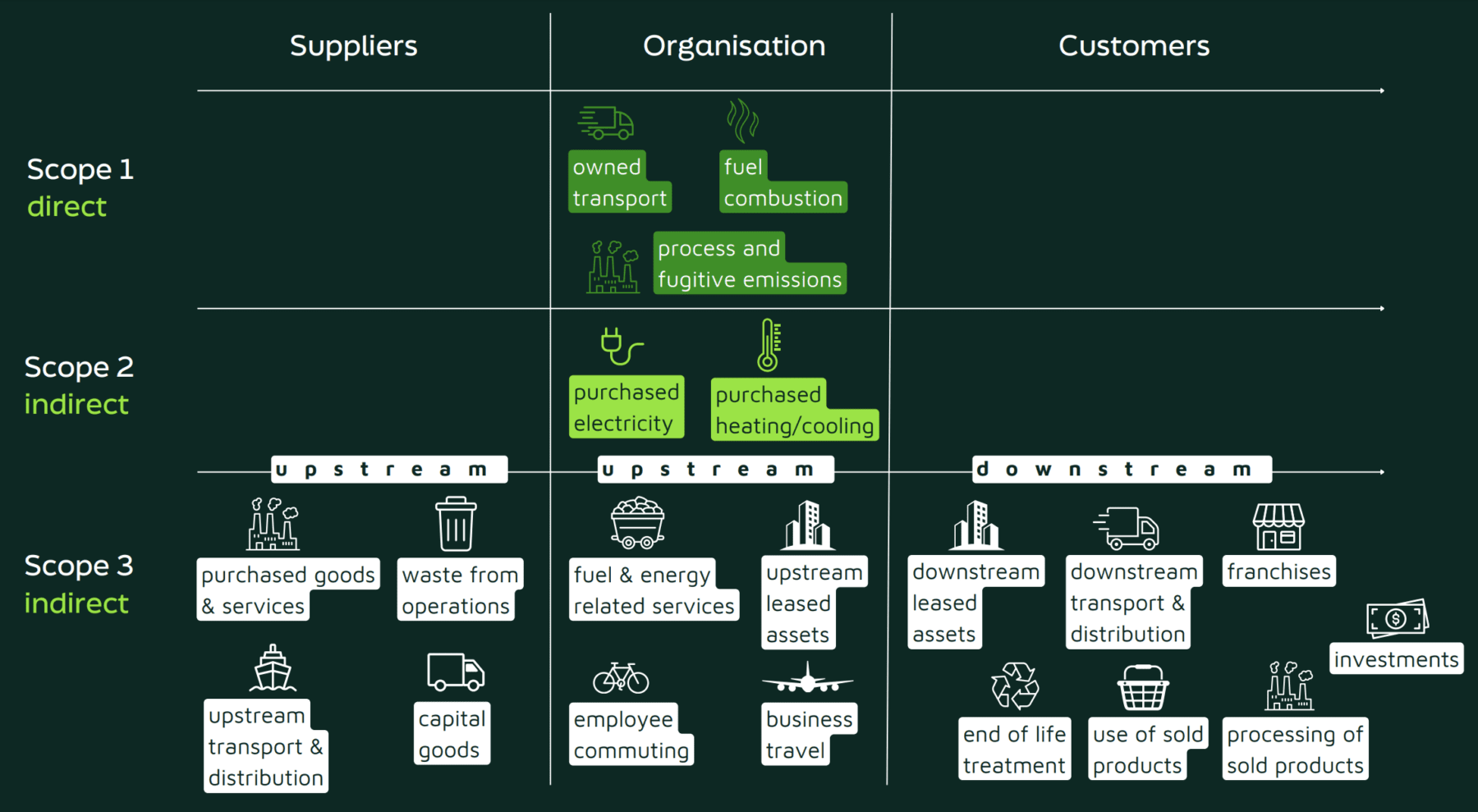
Direct Emissions (Scope 1)
Scope 1 covers carbon emissions that your company produces directly. These are the greenhouse gases released from activities and assets you control. This includes emissions from company vehicles, on-site machinery, and manufacturing processes. It also encompasses any unintended releases of greenhouse gases, such as refrigerant leaks from air conditioning units. As these emissions are under your direct control, they often present the most straightforward opportunities for carbon savings.
Indirect Emissions from Purchased Energy (Scope 2)
Scope 2 refers to emissions associated with the energy your company purchases and uses. While you don’t produce these emissions directly, they’re still attributed to your business due to your energy consumption. This primarily includes electricity, but also covers purchased heating and cooling. Reducing Scope 2 emissions often involves improving energy efficiency or transitioning to renewable energy sources. It’s worth noting that even small changes in energy use can lead to significant reductions in this category.
Other Indirect Emissions (Scope 3)
Scope 3 is the broadest and often the most challenging category. It encompasses all other indirect emissions associated with your company’s activities. This includes upstream emissions from your supply chain (such as the production of goods you purchase) and downstream emissions (like the use and disposal of your products by customers). It also covers areas like employee commuting, business travel, and waste management. Understanding how to calculate Scope 3 emissions can lead to substantial reductions in your overall carbon footprint.
Why doing all of this? Here are some incentives to start with: increased operational efficiencies, cost savings, cost avoidance, customer loyalty, and improved reputation. This might be a new challenge for your business, but environmental consciousness is becoming more and more important. Managing your carbon footprint across all three scopes starts with calculating your carbon emissions.
Calculating your carbon footprint
Understanding how to calculate your carbon footprint is vital for effective climate action. This section guides you through the step-by-step process of calculating your organisation’s carbon emissions accurately. If you have a bigger business with multiple divisions or geographic locations, you may want to repeat this for each division and then consolidate. It’s OK for this to take months, or even longer – the bigger and more complex your organisation is, the more resources it will take.
Gathering Data
The foundation of a reliable carbon footprint measurement lies in comprehensive data collection. Start by gathering information from various sources within your organisation:
- Energy bills (electricity, gas, heating, oil)
- Fuel consumption records for company vehicles
- Business travel data (flights, train journeys, car rentals)
- Waste management reports
- Procurement records of raw materials and supplies
Best practice – establish a systematic approach to collect data. The more detailed and accurate the data, the more precise your carbon calculation will be.
Identify Emission Sources
To capture your full carbon footprint, it’s essential to identify all relevant emission sources across the three scopes:
- Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources (e.g., on-site fuel combustion, company vehicles)
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling
- Scope 3: All other indirect emissions occurring in the value chain (e.g., business travel, employee commuting, waste disposal, purchased goods and services)
Identify these sources will help you in understanding your overall carbon footprint.
Applying Emission Factors
Emission factors are essential in converting activity data into measurable CO2 emissions. These factors represent the amount of greenhouse gases emitted per unit of activity:
- Use reputable sources for emission factors, such as government databases or industry-specific guidelines
- Ensure factors are up-to-date and relevant to your geographic location
- Apply appropriate factors to each emission source identified in the previous step
Using the Carbon Footprint Calculation Formula
The basic formula for carbon calculation is:
Activity Data x Emission Factor = Carbon Emissions (CO2e)
For example, if a company uses 10,000 kWh of electricity, and the emission factor for electricity is 0.233 kg CO2e/kWh, the total carbon emissions would be 2,330 kg CO2e.
Knowing how to calculate CO2 emissions helps businesses make informed decisions to reduce their carbon impact.
Interpreting Your Results
Once you’ve calculated your business’s carbon footprint, the next step is understanding what those numbers mean. The results provide a snapshot of your company’s carbon impact, showing how much carbon is generated by different operations, from energy use to supply chain activities. This insight is essential for developing targeted strategies to reduce emissions and improve sustainability.
Understanding Your Carbon Impact
Your carbon footprint results give you a clear picture of where your company stands in terms of greenhouse gas emissions. If certain areas, like energy use or transportation, show higher emissions, it’s a sign that there might be inefficiencies. Once you know your carbon impact, it’s easier to figure out where to focus your efforts to cut emissions and get your business in line with your environmental goals.
Benchmarking Against Industry Standards
Comparing your carbon footprint to industry standards is a great way to see how your business stacks up against others in your sector. There are tools and reports from industry bodies that offer average emissions data, so you can quickly tell if you’re performing above or below the norm. This kind of benchmarking can really help shape your sustainability plans and set realistic goals for cutting emissions.
Identifying Areas for Carbon Savings
Once you have your results, the next step is identifying where you can make the most significant reductions. Look for areas with the highest emissions, like energy use, transportation, or supply chain operations. Implementing energy efficiency measures, optimising logistics, and working with sustainable suppliers are just a few ways to achieve meaningful carbon savings.
Strategies for Reducing Your Carbon Footprint
Reducing your business’s carbon footprint requires a mix of quick, actionable steps and long-term strategic changes. Whether you’re looking for immediate results or aiming for deeper, lasting impact, implementing both short-term and long-term strategies can help cut emissions while boosting efficiency.
You must be thinking “Isn’t there software to do all this?”
There are plenty of them out there, usually in the category “carbon accounting software”, including this free one from the SME Climate Hub. Let us know on LinkedIn if you’d like us to do a comparison of different options available.
But word is, there is no one size fits all, and the tech is still in its early days although it’s improving quickly with the addition of AI. Gathering data, particularly for Scope 3 supply chain emissions, still requires boots on the ground resource, intimate knowledge about your business, and ideally someone to stay on top of it all.
In our research earlier this year, sustainability professionals highlighted that they’d often rather build their own tools to take into account the complexity of their business models and uniqueness of their industry. One example from the events industry was somebody using purpose-built software that track attendees emissions while travelling to events – quite niche.
The point of all this is there’s no right or wrong approach and you should certainly utilise software – but perhaps reframe it so it is simply bringing speed to your project, don’t expect it to go out and gather the data for you or engage your suppliers – it can’t do that (yet).
Quick Wins for Immediate Carbon Savings
If you’re looking to make quick progress, there are plenty of easy strategies you can put in place right away, without significant investment. One great approach is to find ways to operate more efficiently. For example, by analysing historical data on purchasing patterns, you might identify areas where you can reduce supply orders, cutting both costs and waste. It’s surprising how much carbon you can reduce just by being smarter with what you already have, without needing to make any huge changes. Simple adjustments—like streamlining supply chains or optimising resource use—can have an immediate and measurable impact on both your carbon footprint and your bottom line.
Long-term Strategies for Significant Emissions Reduction
For more substantial carbon savings, you can adopt long-term strategies that require greater investment but offer deeper reductions. Switching to renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can drastically reduce Scope 2 emissions from purchased electricity. Additionally, improving supply chain sustainability by sourcing materials from eco-friendly suppliers and optimising logistics can cut emissions over time. Electrifying your vehicle fleet, improving building insulation, or investing in energy-efficient manufacturing equipment are other long-term solutions that offer meaningful reductions.
The Path to Net Zero
Achieving net-zero emissions is a big long-term goal for many businesses, and it takes a solid plan to get there. Start by setting clear targets for reducing emissions in every part of your operations, making sure you know how to calculate your carbon footprint across Scopes 1, 2, and 3. Focus on cutting emissions in all three areas, and consider investing in renewable energy and carbon capture tech. You can also offset any emissions you can’t avoid. Keep reviewing your progress and adjusting your approach to stay on track toward your net-zero goal.
How Green Ibex Can Help
We are here to guide you every step of the way on your journey to carbon neutrality. We know how daunting it can be to be tasked with a net zero project, especially if this is your first time tapping into sustainability. Our aim is to offer all-in-one service, covering everything net zero from A to Z. We’re ready to support your business through every stage of your sustainability efforts.
Calculating Your Carbon Footprint
Our team of experienced environmental consultants utilises state-of-the-art tools and methodologies to accurately measure your organisation’s carbon emissions:
- Detailed data collection guidance
- Advanced emissions tracking software
- Custom-tailored carbon accounting frameworks
Reducing Emissions
We work closely with you to identify and implement effective carbon reduction strategies:
- Energy efficiency audits and recommendations
- Renewable energy transition planning
- Supply chain optimisation for reduced Scope 3 emissions
Offsetting Residual Emissions
For emissions that cannot be eliminated, we offer high-quality carbon offset solutions:
- Curated portfolio of verified offset projects
- Transparent reporting and tracking of offset investments
- Support in developing internal carbon pricing mechanisms
On-going Support and Expertise
Green Ibex provides continuous assistance to ensure your long-term success:
- Regular progress assessments and benchmarking
- Staff training and capacity building
- Regulatory compliance guidance and reporting support
Let’s talk about how we can help your organisation.
Share this article
Get in touch
Let’s prepare for the future together
We can tailor services to meet your particular needs. Complete the form or email us and and we can discuss your specific requirements.
Registered Address
71-75 Shelton Street,
London,
WC2H 9JQ,
United Kingdom